The stroke unit in the hospital
Contents:
- What is a stroke unit
- What happens in the stroke unit?
- Range of services of a stroke unit
- Typical treatments in the stroke unit
- Certified stroke units in Germany
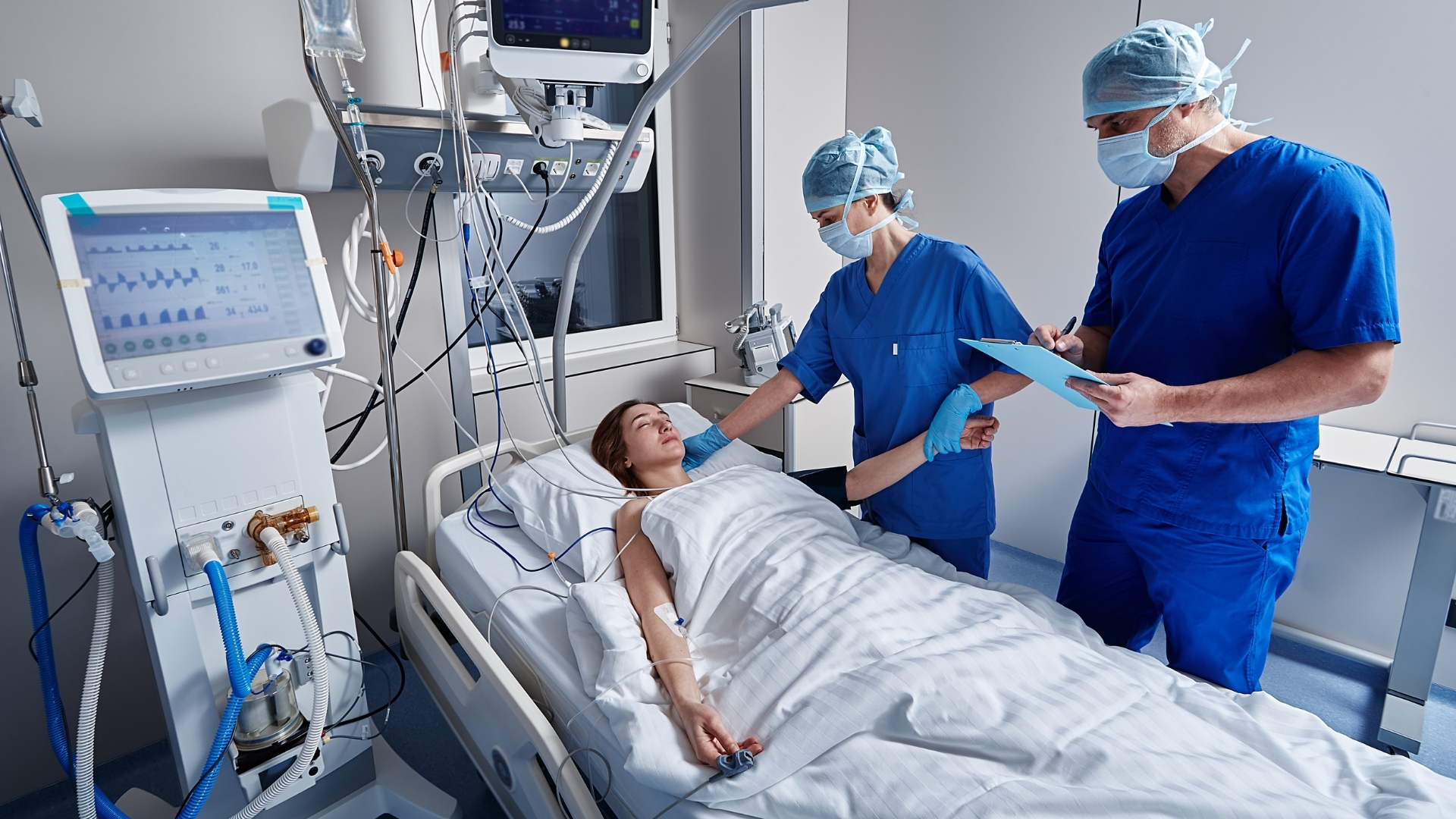
What is a stroke unit?
A stroke unit is a special department just for stroke patients, i.e. a specialized stroke ward. The special feature of these wards is the focus on comprehensive acute therapy for patients. Specialist staff from neurology, cardiology, physiotherapy, speech therapy, occupational therapy and specially trained nursing staff look after those affected around the clock. In this way, complications can be avoided, the cause quickly identified and treatment started immediately. The principle for treatment is “time is brain” – the faster patients are treated, the better their chances of recovery. You can find more information on why this is the case and what exactly happens in the brain during a stroke here.
Most patients stay in the stroke unit for between one and three days, or longer in the case of severe strokes or complications.
What happens in the stroke unit?
A stroke unit is usually linked to a diagnostic center so that imaging procedures can be used and CT or MRI scans can be taken to determine the cause of the stroke. In this way, patients receive all the necessary examinations in the shortest possible time and without having to travel long distances. In addition to MRI and CT, ultrasound examinations of the vessels supplying the brain and targeted cardiac examinations can be carried out to provide the best secondary prophylaxis.
Range of services of a stroke unit

Treatment in a stroke unit includes, among other things
At least 24- to 72-hour monitor monitoring with measurement of cardiac activity, blood pressure and temperature
Care by specially trained nursing staff
Comprehensive clarification of the causes of stroke using imaging procedures such as magnetic resonance imaging or computer tomography, Doppler and duplex sonography examinations of the neck vessels, long-term ECG and ultrasound of the heart
Various blood tests (blood count, blood coagulation, blood sugar levels, electrolyte balance and kidney values)
Regular medical neurological examinations
Early examination and treatment by speech therapists, physiotherapists and occupational therapists
Initiation of further rehabilitation measures
Typical treatments in the stroke unit
Stroke units can perform thrombolysis or thrombectomies to treat ischemic strokes. Thrombolysis, also known as lysis therapy, involves administering a medication that can dissolve the blood clot and thus restore blood flow. Rapid admission to the ward is very important for this therapy, as the medication can only be used in the first few hours after the stroke. Thrombectomy is the surgical removal of a blood clot with the same aim of restoring blood flow. Some larger clinics also have a neurosurgery department. Emergency operations can be carried out there in the event of severe cerebral hemorrhages, for example. If patients have not been admitted to a stroke unit with an associated neurosurgery department, transfers may therefore occur in rare cases.
Certified stroke units in Germany
The term “stroke unit” is not legally protected in Germany. However, there is a list of certified stroke units. These clinics are constantly monitored and are subject to high medical standards. This certification system was introduced by the German Stroke Society. Such clinics occupy a special position and are particularly well networked with specialist staff from other departments. Interdisciplinary networking between those treating patients on the ward ensures that patients can start rehabilitation measures as early as possible. Stroke units also have access to the most modern therapy procedures for stroke treatment.
A list of all stroke units in Germany can be found at:
